
The Project Management Body of Knowledge, which was originally published electronically in March 1987, contains nine knowledge areas as well as 37 processes. The PMBOK Guide, 2000 Edition, contains 211 pages and contains nine knowledge areas and 39 processes. The fourth edition, which contains 467 pages with 47 processes, is the fourth PMBOK Guide. The fifth edition was published December 2012 and includes 619 ITTO. The PMBOK Guide provides a complete set of project management methods and practices that help to manage a project.
Closing projects
There are several stages to project closure. The goal of each phase is to ensure that all tasks have been completed and that the planned work has been completed. This includes the preservation of project information and the release of resources to the organization team. PMbok's closure process makes it easy to manage the final phase of project management. These are the categories of these processes:
A successful project close ties together all components of the project. Leaders who are effective create an inclusive space that is accessible to everyone. They demonstrate to team members how they contributed to the success of the project. The team can understand their role and make the project meaningful by including them in the closure process. The closing phase should offer time for reflection, self-evaluation, and self-evaluation. This step is vital to ensure the success of the project closure process.
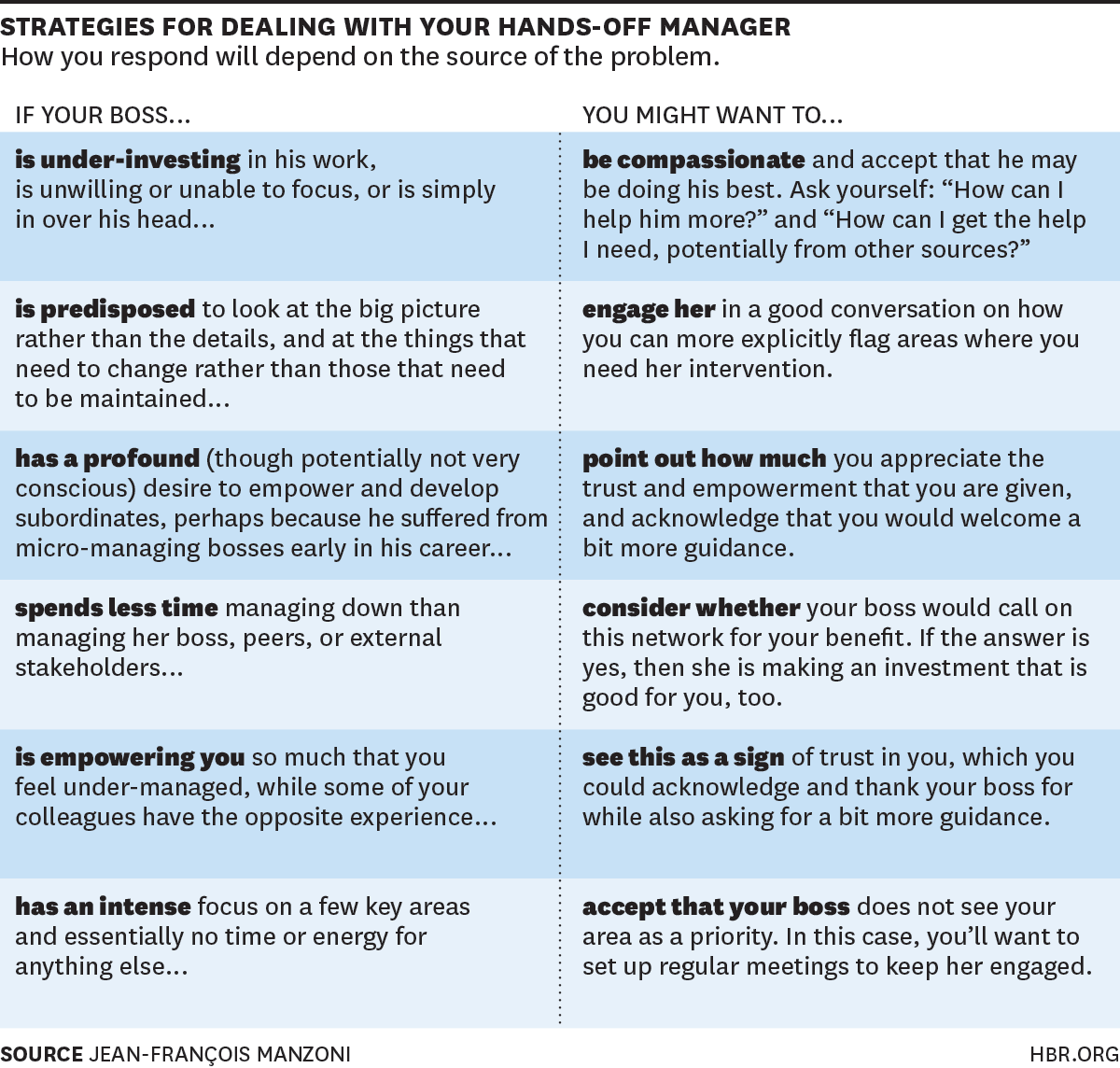
Knowledge areas
The Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBok), defines three Knowledge Areas. These Knowledge Areas will impact the project's success, no matter how well or poorly managed. These areas should be understood as distinct from one another, yet overlap with each other. These areas are critical to the success and sustainability of a project. Knowledge Areas should be based on the best practices of project management. This will assist you in making informed decisions.
The Project Management Knowledge Area includes four processes: Monitoring, monitoring, planning, and identifying risks. These processes are designed to reduce the impact of risks on projects. Project Procurement Management Knowledge Area includes managing stakeholder engagement and conducting procurement controls. This knowledge section is the latest addition of the PMBOK. It's time for you and your knowledge to be updated. Consider updating your knowledge base to meet changing project requirements.
Process groups
The PMBOK Guide recognizes five basic Process Groups. Each process has a role in the overall success of the project. These groups allow project managers to use their PM skills and knowledge in order to achieve project goals. The five Process Groups are related by their outputs. Each process has inputs. As an example, the Initiating Process Group contributes input to the Planning Process Group, which, in turn, provides input for the Executing Process Group.
PMBOK has created knowledge areas to organize processes according the knowledge required. One common knowledge area is "Project Cost Management," though specific tasks such as managing costs can be performed in other parts of the process. Each process group is organized in a logical sequence. You can find more information on each of these groups at the PMBOK Process Groups webpage. This figure illustrates how each process group fits in to the overall project.

Alternatives to PMBOK
It may be worth looking at other alternatives if your current project management system is not working. PMBOK can be a great foundation but doesn't provide everything you need to manage a successful project. There are many other methods that you can use to manage your projects, such as Enterprise Analysis, requirements management and stakeholder management. These alternatives are often more focused on specific aspects of a project, such as business needs, rather than on a particular project type.
PMBOK is a great option if you are interested in using a methodology, but don't have the time to learn it. PMBOK Guide is a collection of best practices, terminology, as well as guidelines that can assist you in managing projects. This guide is a valuable resource for large-scale enterprise projects. It helps to define roles and responsibilities, keeps projects on track, and supports the idea of managing by exception. It can be time-consuming and tedious to use if you manage a small project.
FAQ
What are some common management mistakes?
Sometimes managers make it harder for their employees than is necessary.
They might not give enough support and delegate the right responsibilities to their staff.
Additionally, many managers lack communication skills that are necessary to motivate and direct their teams.
Managers can set unrealistic expectations for their employees.
Managers may attempt to solve all problems themselves, rather than delegating it to others.
What is Six Sigma?
It is a way to improve quality that places emphasis on customer service and continuous learning. The goal is to eliminate defects by using statistical techniques.
Motorola invented Six Sigma in 1986 as part its efforts to improve manufacturing.
The idea spread quickly throughout the industry, and today, many organizations are using six sigma methods to improve product design, production, delivery, and customer service.
What is TQM, exactly?
When manufacturing companies realized that price was not enough to compete, the industrial revolution brought about the quality movement. They needed to improve quality and efficiency if they were going to remain competitive.
In response to this need for improvement, management developed Total Quality Management (TQM), which focused on improving all aspects of an organization's performance. It included continuous improvement processes, employee involvement, and customer satisfaction.
What does it mean to say "project management"
It refers to the management of activities related to a project.
We help you define the scope of your project, identify the requirements, prepare the budget, organize the team, plan the work, monitor progress and evaluate the results before closing down the project.
How can a manager motivate his/her staff?
Motivation is the desire to do well.
You can get motivated by doing something enjoyable.
Another way to get motivated is to see yourself as a contributor to the success of the company.
For example: If you want to be a doctor, you might find it more motivating seeing patients than reading medical books all day.
A different type of motivation comes directly from the inside.
You might feel a strong sense for responsibility and want to help others.
Perhaps you enjoy working hard.
Ask yourself why you feel so motivated.
Then think about how you can make your life more motivating.
Statistics
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do I do the Kaizen Method?
Kaizen means continuous improvement. Kaizen is a Japanese concept that encourages constant improvement by small incremental changes. It is a process where people come together to improve their processes.
Kaizen is one the most important methods of Lean Manufacturing. This concept requires employees to identify and solve problems during manufacturing before they become major issues. This is how you can improve the quality and lower the cost.
Kaizen is about making everyone aware of the world around them. If something is wrong, it should be corrected immediately so that no problem occurs. So, if someone notices a problem while working, he/she should report it to his/her manager.
Kaizen follows a set of principles. Start with the end product, and then move to the beginning. In order to improve our factory's production, we must first fix the machines producing the final product. We then fix the machines producing components, and the machines producing raw materials. We then fix the workers that work with those machines.
This is why it's called "kaizen" because it works step-by-step to improve everything. Once we have finished fixing the factory, we return to the beginning and work until perfection.
To implement kaizen in your business, you need to find out how to measure its effectiveness. There are many ways to tell if kaizen is effective. Another way to determine if kaizen is working well is to look at the quality of the products. Another method is to determine how much productivity has improved since the implementation of kaizen.
A good way to determine whether kaizen has been implemented is to ask why. It was because of the law, or simply because you wanted to save some money. It was a way to save money or help you succeed.
If you answered yes to any one of these questions, congratulations! You're ready to start kaizen.